Location intelligence (LI) is transforming industries by enabling smarter decision-making, optimized operations, and personalized experiences. Whether you’re ordering a ride, tracking a delivery, or determining the best site for a new business, location intelligence plays a vital role in shaping the modern landscape. But how does it actually work? In this blog post, we will explore the inner workings of location intelligence, its technologies, applications, and the future potential it holds.
- What is Location Intelligence
- The Building Blocks of Location Intelligence
- Applications of Location Intelligence
- The Future of Location Intelligence
- Conclusion
What is Location Intelligence?
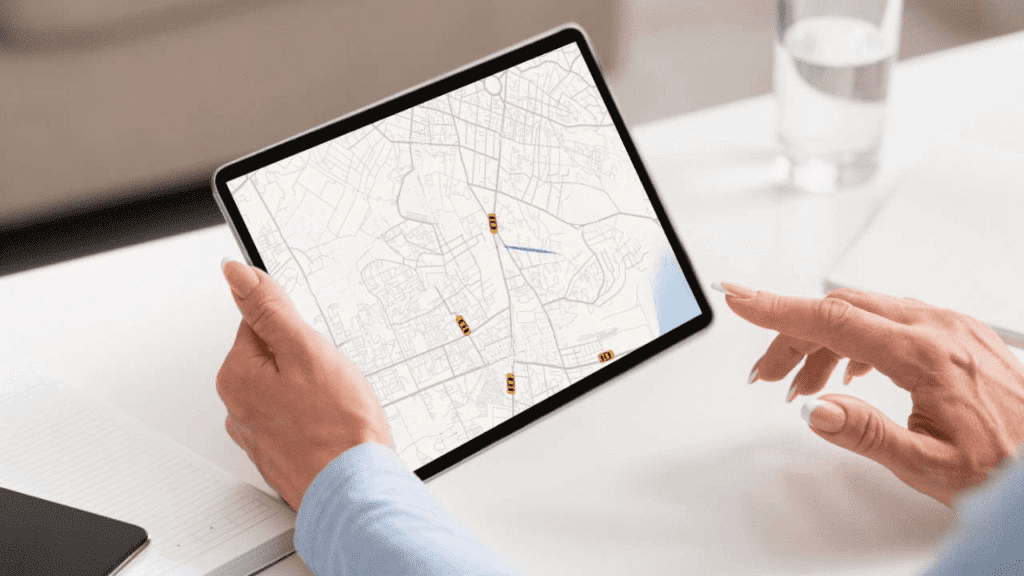
Location Intelligence (LI) refers to the process of using geographic data to gain insights that inform decision-making and strategy. It combines spatial data with business intelligence tools to help organizations understand patterns, trends, and behaviors tied to specific locations. Simply put, LI transforms raw geographic data into actionable intelligence.
The foundation of LI is geographic information system (GIS) technology, which is used to collect, analyze, and visualize spatial data. By integrating this data with real-time sources, such as GPS, social media, or weather, businesses can gain a clearer picture of how location influences various outcomes.
The Building Blocks of Location Intelligence
To understand how location intelligence works, it’s crucial to break down the key technologies that enable it:
1. Geospatial Data
Geospatial data is the backbone of location intelligence. This data includes any information that is associated with a geographic location. It can be gathered from various sources, including satellite imagery, GPS coordinates, mobile devices, maps, and even IoT sensors. The data is typically stored in a format that allows it to be analyzed with geographic tools.
There are two main types of geospatial data:
- Vector Data: Points, lines, and polygons representing features like roads, buildings, and city boundaries.
- Raster Data: Pixel-based data, often used for satellite imagery or aerial photography.
2. Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
At the core of location intelligence is GIS technology. GIS is a framework for gathering, managing, and analyzing spatial data. It allows organizations to create detailed maps, analyze trends, and visualize complex spatial relationships.
GIS can be used for:
- Mapping: Creating detailed visual maps that represent different variables (e.g., population density, traffic patterns).
- Analysis: Identifying patterns in data, such as where traffic congestion occurs or which areas are most vulnerable to natural disasters.
- Modeling: Creating predictive models, such as forecasting the future development of certain geographic areas.
3. Real-Time Data Sources
Modern location intelligence goes beyond static maps by incorporating real-time data. This includes information from sources like:
- GPS devices: Used by vehicles, smartphones, and other IoT devices to track precise locations.
- Sensors: From traffic monitoring systems to weather stations, real-time data helps organizations respond dynamically.
- Social Media: Tweets, posts, and check-ins provide a wealth of location-based information that can reveal public sentiment, trends, and behaviors.
4. Data Analytics and AI
Data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) play an essential role in interpreting the massive volumes of location data. With the help of machine learning algorithms, businesses can uncover insights from geospatial data that would be otherwise difficult to spot manually.
AI-powered tools can:
- Analyze Patterns: For example, AI can identify the best locations for a new store based on customer activity, demographics, and foot traffic.
- Predict Trends: Machine learning models can predict how certain geographic locations will evolve, such as predicting the impact of a new development or the spread of a disease.
- Personalize Services: Companies use AI to tailor services based on the customer’s current location, like offering discounts or recommendations when a customer enters a store.
5. Cloud Computing
Cloud technology enables the storage and processing of enormous amounts of geospatial data. It offers scalability, real-time collaboration, and access to powerful computational tools that would be difficult to manage on-premises. Many businesses rely on cloud-based platforms to store and analyze location data, ensuring they can access insights from anywhere, at any time.
How Does Location Intelligence Work?
Now that we understand the core components, let’s take a look at the typical workflow of location intelligence.
1. Data Collection
The first step in the location intelligence process is data collection. This involves gathering geographic information from multiple sources, such as GPS signals, satellite imagery, public datasets, IoT devices, and more. Depending on the business needs, data can be collected at varying levels of granularity, from global data to hyper-local data (e.g., foot traffic in a specific store).
2. Data Integration and Processing
Once collected, the data is integrated into a unified system. This may involve cleaning and transforming raw data into a usable format, making it ready for analysis. With the help of GIS and cloud platforms, businesses can consolidate diverse data sources, including customer transaction data, sensor data, and demographic information, into a comprehensive geographic database.
3. Data Analysis and Visualization
With all the data at hand, the next step is to apply analytics and AI tools to derive insights. Analysts use geospatial analysis tools to detect patterns in location data. For example, they might analyze traffic congestion data to suggest optimal delivery routes or evaluate customer behaviors to pinpoint locations with high demand for certain services.
Advanced data visualization techniques, like heatmaps, 3D maps, and interactive dashboards, help decision-makers easily understand the findings. For example, businesses can visualize where most of their customers are located, which areas experience high sales, or which regions are underserved.
4. Decision-Making
With actionable insights in hand, businesses can make data-driven decisions. For example, a retail chain may use location intelligence to choose the best location for a new store by analyzing factors like foot traffic, nearby competitors, and local demographics.
Similarly, logistics companies use location intelligence to optimize delivery routes, reduce fuel costs, and improve overall efficiency. Meanwhile, city planners can use LI to evaluate infrastructure needs and make urban development decisions.
5. Action and Monitoring
The final step involves taking action based on the insights derived from location data. Whether it’s adjusting marketing strategies, improving logistics, or expanding operations, the decision is executed. Location intelligence doesn’t stop at decision-making; businesses also need to continuously monitor outcomes. By tracking the impact of decisions, companies can refine their strategies in real-time and adapt to changing conditions.
Applications of Location Intelligence
Location intelligence is reshaping several industries with its vast range of applications. Here are some notable examples:
1. Retail and Real Estate
Retailers and real estate companies use location intelligence to find optimal locations for stores or properties. By analyzing foot traffic patterns, demographics, and competitor locations, they can select sites that maximize customer engagement and profitability.
2. Logistics and Transportation
Location intelligence is crucial in optimizing transportation routes and reducing operational costs. For example, logistics companies like FedEx and UPS use real-time location data to plan the most efficient delivery routes, while ride-hailing apps like Uber use LI to match drivers with riders in real-time.
3. Urban Planning and Smart Cities
Location intelligence supports urban planners in building smarter cities. By analyzing traffic patterns, infrastructure usage, and population growth, city planners can allocate resources effectively and plan future developments. LI is also key in the development of smart city solutions, such as intelligent traffic management and energy-efficient services.
4. Healthcare
In healthcare, location intelligence helps hospitals and clinics optimize service delivery. By analyzing patient data, geographic location, and real-time factors like traffic and weather, healthcare providers can ensure resources are allocated efficiently, reducing wait times and improving patient outcomes.
5. Marketing and Advertising
Businesses are increasingly using location-based data to target customers with personalized promotions. For example, geofencing technology allows businesses to send tailored offers to users’ smartphones when they enter a particular location. This improves customer engagement and boosts sales.
The Future of Location Intelligence
As location intelligence continues to evolve, the future looks incredibly promising. Advances in AI, 5G networks, and IoT are expected to increase the volume and accuracy of location data, further enabling businesses to make real-time, informed decisions.
Key trends include:
- Increased Automation: Automation powered by AI and machine learning will allow businesses to act on insights in real-time, improving operational efficiency and reducing costs.
- Augmented Reality (AR): The integration of location data with AR technologies will transform consumer experiences, enabling real-time, location-based navigation and immersive shopping experiences.
- Enhanced Data Privacy: As location data becomes increasingly personal, there will be a growing emphasis on data privacy and security, with businesses needing to ensure that they handle location data responsibly.
Conclusion
Location intelligence is a powerful tool that is revolutionizing the way businesses and governments operate. By combining geographic data with advanced analytics and AI, organizations can make smarter decisions, optimize processes, and create personalized experiences. As technology continues to advance, location intelligence will only grow more sophisticated, helping businesses navigate the complexities of an increasingly interconnected world. Understanding how location intelligence works is key to unlocking its potential and staying ahead in an ever-evolving digital landscape.